1. The role and application of PVC injection molding machine
As the core equipment of the plastic processing industry, PVC injection molding machine plays a vital role in today's industrial manufacturing field. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), as a versatile, cost-effective and durable thermoplastic material, is widely used in many fields such as construction, medical, automobile and consumer goods through injection molding process.
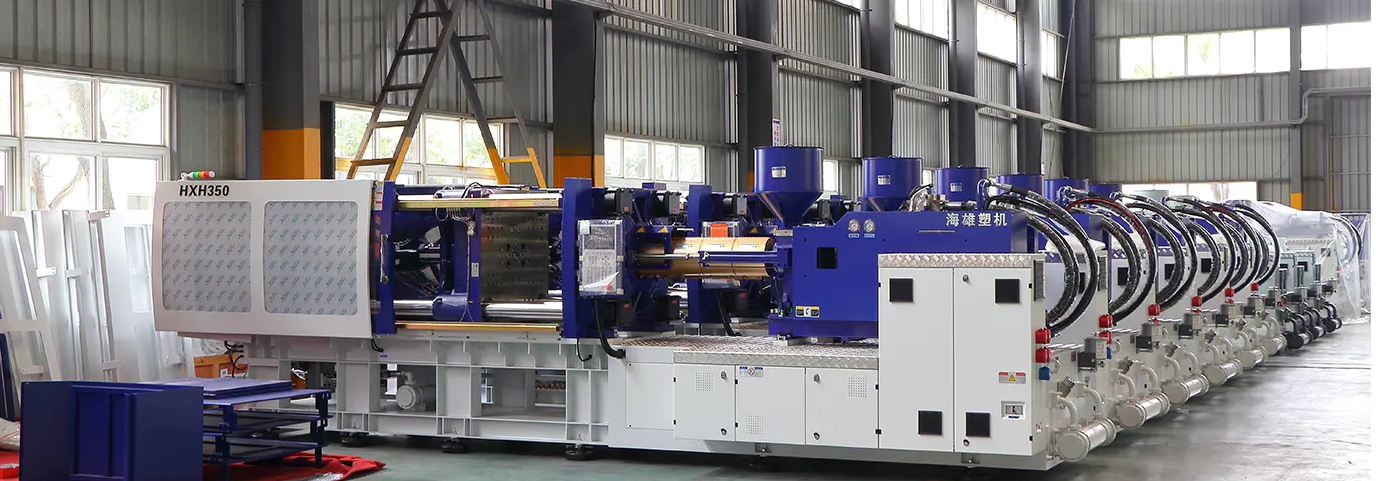

PVC injection molding machine is a special injection molding equipment specially used for processing polyvinyl chloride materials, which occupies an irreplaceable position in the plastic processing industry. According to industry data statistics, about 23% of the world's plastic injection molding production involves PVC materials, especially in the fields of building pipes, medical equipment and wires and cables, the application ratio of PVC injection molding machines is as high as more than 60%. Behind this wide application is the unique performance advantages of PVC materials themselves and the efficient combination of injection molding process.
The main function of PVC injection molding machine is to transform raw materials into plastic products with precise size and functional characteristics through three key stages: heating plasticization, high-pressure injection and mold molding. Compared with general injection molding machines, PVC injection molding machines are optimized for the characteristics of PVC materials, and can effectively overcome the technical difficulties in PVC processing, such as poor thermal stability, high melt viscosity, and easy decomposition. In the construction industry, pipe fittings, joints, and door and window accessories produced by PVC injection molding machines have excellent weather resistance and chemical stability; in the medical field, products such as infusion bags and catheters molded by PVC injection molding meet strict biocompatibility requirements.
From the perspective of the industrial chain, PVC injection molding machines are in the middle link between raw materials and terminal applications, and their technical level directly affects the quality and production cost of the final product. A qualified PVC injection molding machine is usually composed of key components such as injection system, mold clamping system, hydraulic system, control system, and temperature control system. The coordinated work of these systems ensures that PVC materials can complete the molding process under optimal conditions. With the improvement of environmental protection requirements and the growth of medical needs, PVC injection molding machines are developing in a more precise, energy-saving and intelligent direction.
The industry specificity of PVC injection molding machines is also reflected in their adaptability to material formulations. PVC, as a plastic whose properties can be adjusted by additives, is divided into two categories: rigid PVC (RPVC) and flexible PVC (FPVC). Rigid PVC has high strength and rigidity and is often used in building materials; while flexible PVC becomes soft and elastic due to the addition of plasticizers, and is suitable for products such as medical pipes. PVC injection molding machines need to be able to handle these two significantly different types of materials, which requires the equipment to have a wider process window and more flexible parameter adjustment capabilities. At the same time, with the increasingly stringent environmental regulations, the application of lead-free stabilizers and new environmentally friendly plasticizers has also put forward new technical requirements for PVC injection molding machines.
In terms of economic benefits, PVC injection molding machines provide manufacturers with highly competitive production solutions. Compared with metal processing or other plastic molding processes, PVC injection molding has the advantages of short cycle, high material utilization, and low labor demand, which is particularly suitable for the production of large-scale standardized products. Taking PVC pipe fittings in the construction industry as an example, the daily production capacity of a medium-sized PVC injection molding machine can reach 5,000-8,000 pieces, and the product weight error can be controlled within ±0.5%. Such accuracy and efficiency are difficult to achieve with other processes. In addition, PVC injection molding machines also have the characteristics of long mold life (usually up to 500,000 to 1 million times) and relatively low energy consumption (about 40% energy saving compared to metal die casting), which further reduces production costs.
With the continuous development of the trend of "plastic replacing steel", the importance of PVC injection molding machines will be further highlighted. Especially in the application field of pursuing lightweight, corrosion resistance and cost control, PVC injection molding products are constantly replacing traditional materials. As the key equipment to achieve this transformation, the technological innovation and market expansion of PVC injection molding machines will continue to attract industry attention.
2. Working principle and process flow of PVC injection molding machines
The working principle of PVC injection molding machines is based on the molding characteristics of thermoplastics. By precisely controlling parameters such as temperature, pressure and speed, PVC raw materials are converted into products of the desired shape. This process integrates multidisciplinary technologies such as mechanical engineering, materials science and automatic control to form a complex and precise processing system. Understanding the working principle of PVC injection molding machines is crucial to optimizing production processes and improving product quality.
System composition and function
PVC injection molding machine is mainly composed of five systems: injection system, clamping system, hydraulic system, control system and temperature control system. The injection system is responsible for the plasticization and injection of PVC materials. It is the core part of the equipment and includes key components such as hopper, barrel, screw and nozzle. Unlike general injection molding machines, the screw of PVC injection molding machine usually has a special design, with a small length-to-diameter ratio (L/D) (generally between 18:1 and 22:1) and a low compression ratio (about 1.8-2.5) to reduce the shear heat input to heat-sensitive PVC materials. The clamping system provides mold opening and closing and clamping force to ensure that the mold is not pushed open by the melt pressure during the molding process. Its structural forms include toggle type, hydraulic type and electric type. The hydraulic system provides power for the whole machine and controls the movement of each actuator; the control system is responsible for parameter setting, program control and process monitoring; the temperature control system maintains the precise temperature of the barrel and mold, which is particularly important for heat-sensitive materials such as PVC.
Working cycle analysis
PVC injection molding is a cyclical process, and each cycle contains a series of orderly actions. According to industry standards, a complete working cycle includes the following stages: mold closing → injection → pressure holding → cooling → plasticization → mold opening → ejection of products.
In the mold closing stage, the mold is closed under high pressure, and the clamping force is calculated based on the product projection area and injection pressure, usually 30-80MPa. In the injection stage, the screw moves forward to inject the molten PVC at the front end of the barrel into the mold cavity at high pressure (usually 80-180MPa) and high speed. This process lasts for several seconds, and the injection speed can be controlled in sections to adapt to complex product structures. Maintaining a certain pressure in the pressure holding stage to replenish the material reduced due to cooling shrinkage is crucial to the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the product. The cooling stage allows the product to solidify in the mold, and the time depends on the wall thickness and cooling efficiency. In the plasticization stage, the screw rotates to transport and melt the new material forward to prepare for the next cycle, and retreats to the set position at the same time. Finally, the mold opens, and the ejection mechanism demolds the product to complete a cycle.
Table: Typical process parameter ranges for PVC injection molding
|
Parameter category |
Rigid PVC (RPVC) |
Soft PVC (FPVC) |
Key impact |
|
Barrel temperature(℃) |
160-190 |
150-180 |
Melt fluidity, thermal decomposition risk |
|
Mold temperature (℃) |
30-50 |
20-40 |
Cooling rate, surface gloss |
|
Injection pressure (MPa) |
80-150 |
70-130 |
Mold filling integrity, internal stress |
|
Holding pressure (MPa) |
40-80 |
30-60
|
Shrinkage, dimensional accuracy |
|
Screw speed (rpm) |
30-70 |
25-60
|
Plasticization quality, shear heat |
|
Back pressure (MPa) |
3-10 |
2-8 |
Melt density, plasticization efficiency |
- Peculiarities of PVC Processing
PVC injection molding has significant process differences compared with general plastics such as PP and PE, which is mainly due to the material properties of PVC. PVC has poor thermal stability and is easily decomposed to release hydrogen chloride (HCl) at high temperatures. Therefore, the processing temperature window is narrow, usually controlled within the range of 150-190°C, which is much lower than its theoretical decomposition temperature (about 210°C). To meet this challenge, PVC injection molding machines are usually equipped with more precise temperature control systems, with a zone temperature control accuracy of up to ±1°C, and a special screw design to reduce shear heating. At the same time, PVC melt has high viscosity and poor flow properties, requiring higher injection pressure (usually 20-30% higher than PP) to fully fill the mold. In addition, additives in PVC formulas such as stabilizers and lubricants may form deposits in the barrel, so PVC injection molding machines require more frequent cleaning and maintenance.
- Principles of Plasticization and Injection
The plasticization process of PVC is a complex process of physical state transformation. After solid PVC particles enter the barrel from the hopper, they undergo a transformation from glassy state, high elastic state to viscous flow state under heating and shearing. The rotation of the screw generates a drag flow to transport the material forward, while the shearing action and external heating gradually melt the PVC. Since PVC is a polar material, its melting behavior is different from that of non-polar plastics such as PE, and requires higher energy input. At the end of plasticization, the molten PVC accumulates at the front end of the screw, pushing the screw back to the set position. In the injection stage, the screw is transformed into a plunger, and the melt is injected into the mold cavity at a constant speed or segmented speed under the push of the hydraulic cylinder. The flow behavior of the PVC melt in the mold cavity is affected by the mold temperature, runner design and injection parameters. Reasonable process settings can avoid defects such as spray marks and weld lines.
- Key points of process control
Successful PVC injection molding depends on precise control of key parameters. Temperature control is the primary factor. The barrel is usually divided into 3-5 temperature zones. The temperature gradient rises from the feed port to the nozzle, but the maximum temperature does not exceed 190°C to prevent decomposition. The injection speed affects the melt filling mode and molecular orientation. Thick-walled products should be filled at a low speed to reduce residual stress, while thin-walled parts require high-speed injection to prevent premature coagulation. The setting of holding pressure and time directly affects the shrinkage rate and dimensional stability of the product, and needs to be optimized according to the product structure and material properties. The cooling time accounts for 60-70% of the entire cycle. Optimizing the design of cooling water channels can improve production efficiency. PVC injection molding machines mostly use closed-loop control systems to monitor and adjust these parameters in real time to ensure process stability and product consistency.
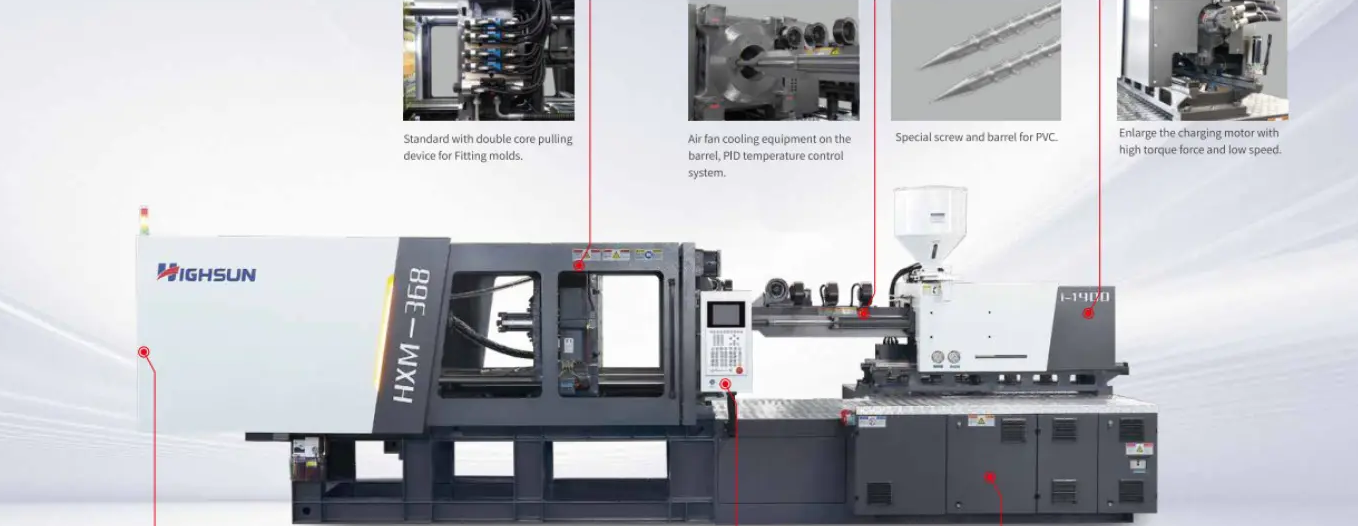
The working principle of PVC injection molding machines embodies the perfect combination of mechanical design and material science. By precisely controlling thermodynamic and rheological processes, PVC raw materials are converted into plastic products with different functions. Mastering these principles is the theoretical basis for optimizing production processes and solving quality problems.
3. Equipment characteristics and technical advantages of PVC injection molding machine
As a type of special plastic processing equipment, PVC injection molding machine has a series of unique designs that match the material properties. These features enable it to show significant technical advantages when processing PVC materials. From mechanical structure to control system, every link of PVC injection molding machine reflects the careful design for the special needs of PVC processing.
- Special screw design
The core feature of PVC injection molding machine is its special screw structure. Compared with ordinary injection molding machine screws, PVC special screws have the following characteristics: small aspect ratio (L/D) (usually between 18:1 and 22:1), reducing material residence time; low compression ratio (about 1.8-2.5), suitable for PVC powder or easily compressible particles; deep screw groove, reducing shear rate and friction heat generation; adding barrier section or mixing head to improve melt uniformity. This design effectively solves the problem of poor thermal stability of PVC and prevents overheating and decomposition of materials during plasticization. The screw material is usually made of double alloy steel or specially surface treated to improve wear resistance and corrosion resistance to cope with HCl acid gas that may be generated during PVC processing. In addition, the speed range of the screw of the PVC injection molding machine is relatively narrow (usually 30-70rpm), and it can be precisely controlled to avoid excessive shearing caused by too high speed.
- Optimization of temperature control system
 ENG
ENG  English
English русский
русский Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى









 +86-188 6861 6288
+86-188 6861 6288 haixiong@highsun-machinery.com
haixiong@highsun-machinery.com No.36 Yongjiang South Road, Beilun District. Ningbo City, 315800, China
No.36 Yongjiang South Road, Beilun District. Ningbo City, 315800, China