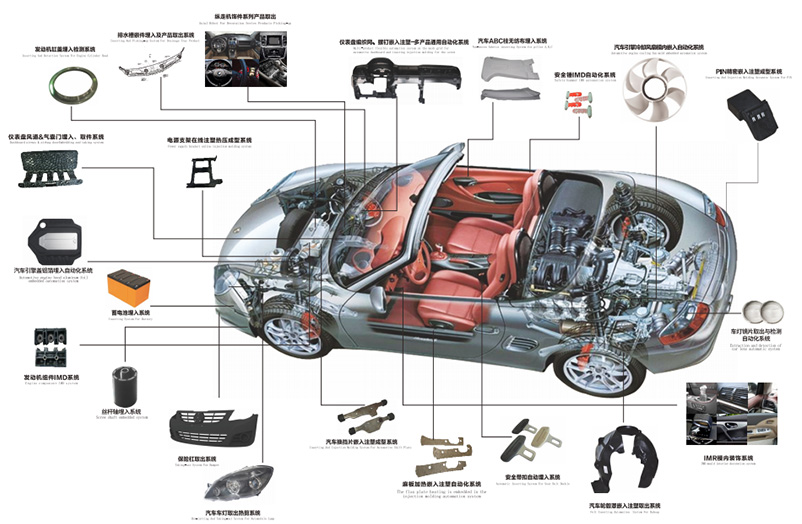
Exterior Parts:
Front/Rear Bumpers
Grilles
Spoilers
Wheel Arches / Fender Flares
Door Handles
Lamp Housings/Lenses
Mirror Housings
Side Skirts
Electrical & Electronic (E/E) Parts:
Sensor Housings/ Sensor Casings
Control Unit Housings/
ECU (Electronic Control Unit) Casings
Relay Boxes
Various Connectors
|
Interior Parts: |
Functional/Structural Parts: |
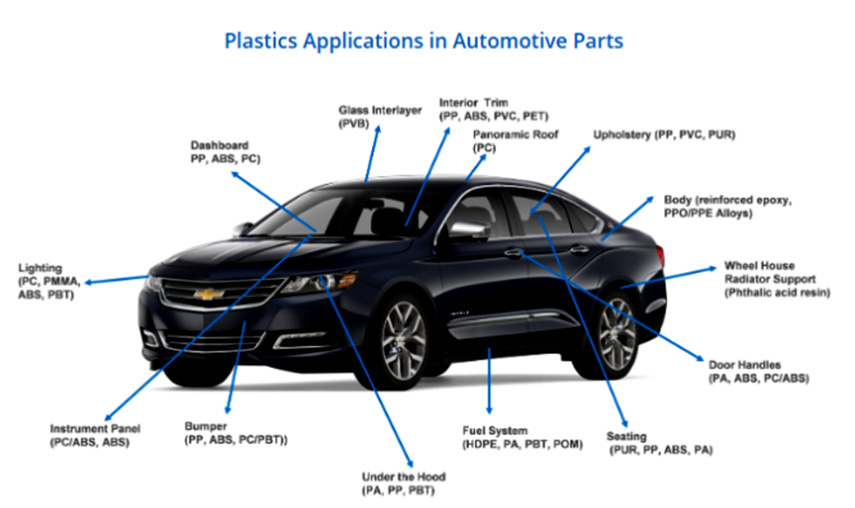
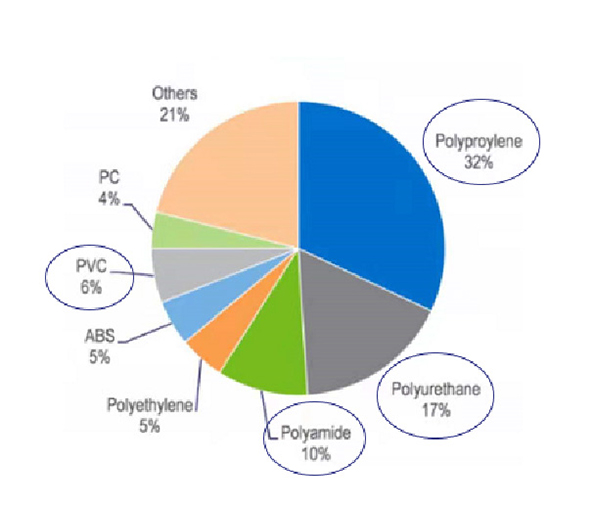
The automotive industry is the third most important consuming sector of polymers after packaging and building & construction. Therefore, changes in the material usage can have major implications on polymer demand and the financial performance of polymer producers.Currently, there are about 30,000 parts in a vehicle, out of which 1/3 are made of plastic. In total, about 39 different types of basic plastics and polymers are used to make an automobile. More than 70% of the plastic used in automobiles comes from four polymers: polypropylene, polyurethane, polyamides and PVC.
→Automotive parts demand exceptionally high dimensional accuracy/tolerance.
→Material diversity complicates process development and elevates material costs.
→Injection molding is energy-intensive, with significant energy cost contributions
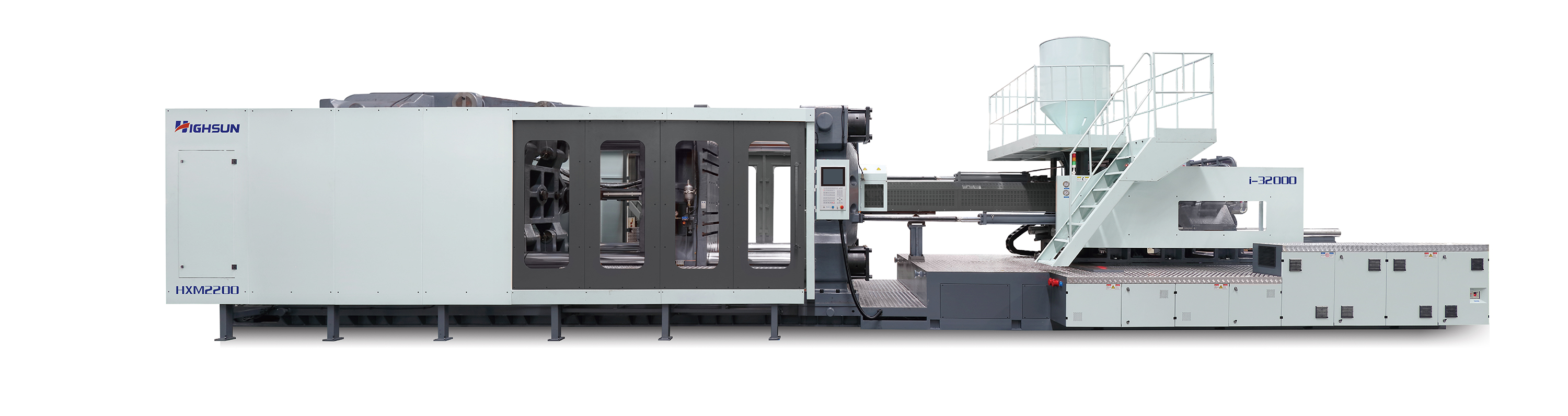 HXM servo machine
HXM servo machine  Intelligent Servo Drive
Intelligent Servo Drive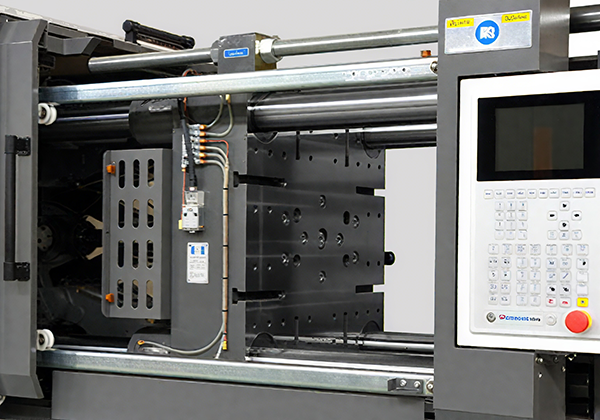 T-Type High-Rigidity Platen System
T-Type High-Rigidity Platen System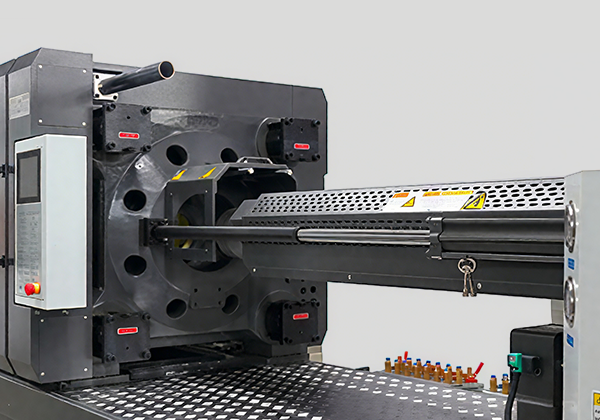 Thermal Management Opti-
Thermal Management Opti- HXZ Two-platen Machine
HXZ Two-platen Machine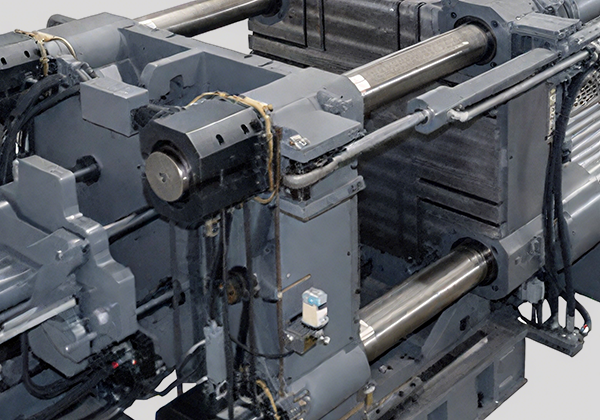 Compact Structure,
Compact Structure,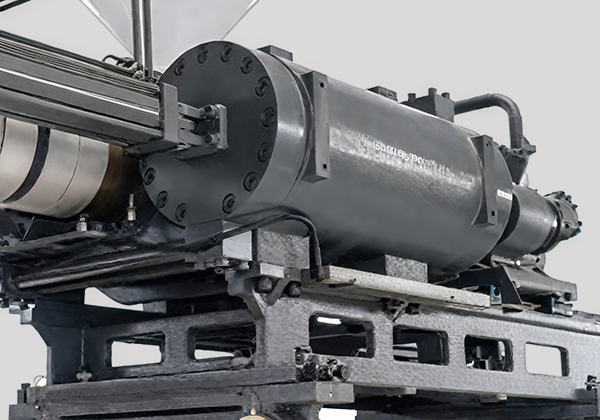 Specialized Screw
Specialized Screw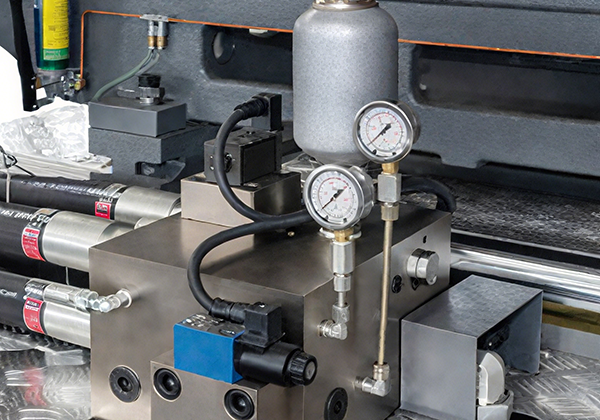 Energy-Efficient & High-Perfor-
Energy-Efficient & High-Perfor-● Raw Material Selection
● Product Design
● Mold Flow Analysis
● Mold Design Recommendations
● Product Performance
● Product Quality
● User-Friendliness
● Safety Requirements
● Production Line Flow
● Layout, Man, Macie Marcrdng according to Process Flow
● Peripheral Automation
● Smart Connectivity
● Professional Installation and Commissioning
● On-Site Operator Training
● Molding Process Training
● Preventive Maintenance (PM)
● Equipment Upgrade